Pain in the Nation 2023: U.S. Death Rate Due to Alcohol, Drugs, and Suicide Increased by 11 Percent in 2021
TFAH’s annual report found that in 2021 increases in death rates due to substance misuse and suicide occurred among all ages, races, and geographic groups, but were particularly high for youth suicides and drug overdose among certain populations of color and in rural parts of the country.
(Washington, DC – May 24, 2023) – The rate of U.S. deaths due to alcohol, drugs, and suicide climbed 11 percent in 2021. While an all-time record, 209,225 Americans lost their lives due to alcohol, drugs or suicide during the year, these deaths continued a two-decade trend of sharply increasing fatalities due to substance misuse and suicide in the U.S.
The 2021 data showed that substance misuse and suicide deaths were up across the U.S. population, with the largest increases occurring among certain populations of color as well as people living in the South, West, and rural regions of the country.
- Drug overdose deaths increased by 14 percent between 2020 and 2021, with larger increases among Native Hawaiians and Pacific Islanders, American Indian/Alaska Native people, and among youth and older adults. For the year, drug overdose rates were highest among adults ages 35 to 54, males, Black people, and young adults ages 18 to 34.
- Alcohol-induced deaths increased by 10 percent between 2020 and 2021, with the highest increases among Native Hawaiians and Pacific Islanders, Latino people, and American Indian/Alaska Native people.
- Suicide mortality increased by 4 percent between 2020 and 2021, with the highest increases among American Indian/Alaska Native people and Black people.
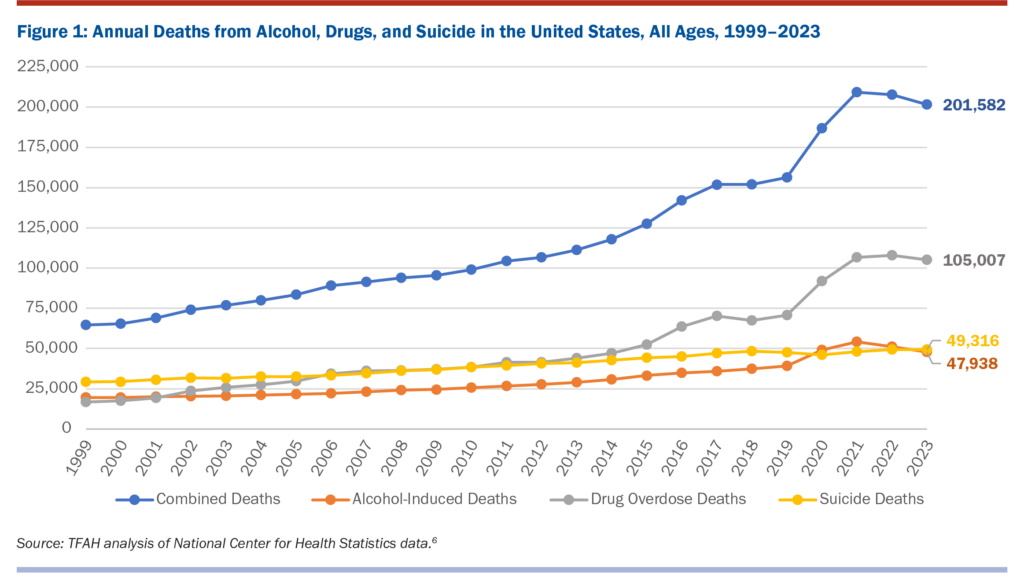
Two Decades Overview
Deaths due to alcohol, drugs, and suicide have been on the rise for over two decades, doubling over the period from 104,379 deaths in 2011 to 209,225 in 2021. Between 2016 and 2021, the escalation in the rate of drug overdose deaths was more than 60 percent. These increases disproportionately impacted Black and Latino populations.
Most of the upturn in deaths due to drug overdose involved opioid overdose, with additional deaths due to cocaine and psychostimulants. In addition, a new and growing threat is xylazine, a tranquilizer approved for veterinary use but mixed with fentanyl to create a highly toxic illicit drug combination.
During the last two decades alcohol and suicide deaths have also increased, but not as sharply as drug deaths.
Youth Suicide Risk
Over the last decade, alcohol, drug, and suicide deaths among youth ages 10 to 17 increased by 65 percent. While youth have a much lower suicide rate than the general population, the upward trend of youth suicide, beginning well before the COVID-19 pandemic, is a startling 71 percent increase between 2010 and 2021. Unlike for other age groups, an increase in suicide deaths among young people was the primary driver for the age group’s increased overall mortality.
American Indian/Alaska Native and LGBTQ youth are most at risk for poor mental health and suicidal behaviors.
Veteran Suicide Risk
Veteran suicide risk also needs immediate attention. The suicide mortality rate for veterans, 32 deaths per 100,000 veterans in 2020, is a much higher rate than the general population.
“The data continue to show alarming increases in deaths due to substance misuse and suicide,” said J. Nadine Gracia, M.D., MSCE, President and CEO of Trust for America’s Health.
“What is needed is urgent and sustained investment in policies and programs that prevent the root causes of substance misuse and suicidality. We need to prevent adverse childhood experiences and trauma and support mental health services in schools, within healthcare settings, and in community settings for all populations,” Gracia said.
Evidence-based Programs Can Help Reverse Deaths of Despair Trends
In response to the growing deaths of despair crisis, a multifaceted approach to improving mental health and well-being in every community is needed. The report includes recommendations for steps federal, state, and local government and other stakeholders should take to address substance misuse and suicide deaths. The recommendations include:
- Invest in prevention programs and conditions that promote health including programs that prevent or reduce adverse childhood experiences and provide trauma-informed services, student mental health services in schools, and strengthened crisis intervention programs, including the 988 crisis lifeline.
- Prevent substance misuse and overdose by supporting syringe service programs, increasing naloxone and fentanyl test strips availability, and expanding funding for the Drug-Free Communities Support Program to bolster prevention programs for youth.
- Transform the mental health and substance use prevention system by increasing access to mental health and substance use healthcare through full enforcement of the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act, integrating mental health and substance use treatment with other healthcare services, and expanding culturally and linguistically appropriate care for populations of color and other underserved populations.

