Ready or Not 2022: Protecting the Public’s Health from Diseases, Disasters, and Bioterrorism
TFAH's Ready or Not report series provides an annual assessment of states' level of readiness to protect the public's health during emergencies. This year's report placed fewer states in the top performance tier for public health preparedness as compared to the 2021 report. The COVID-19 pandemic illustrates the critical need to invest in public health infrastructure and the social determinants of health.
TFAH's Ready or Not report series provides an annual assessment of states' level of readiness to protect the public's health during emergencies. This year's report placed fewer states in the top performance tier for public health preparedness as compared to the 2021 report. The COVID-19 pandemic illustrates the critical need to invest in public health infrastructure and the social determinants of health.
(Washington, DC – March 10, 2022) – TFAH’s Ready or Not 2022: Protecting the Public’s Health from Diseases, Disasters, and Bioterrorism report calls for urgent investment to create a public health system able to protect all Americans’ health during emergencies. The report measures states’ performance on 10 key emergency preparedness indicators, identifies gaps in states’ readiness to respond to emergencies, and includes policy recommendations for strengthening the nation’s health security.
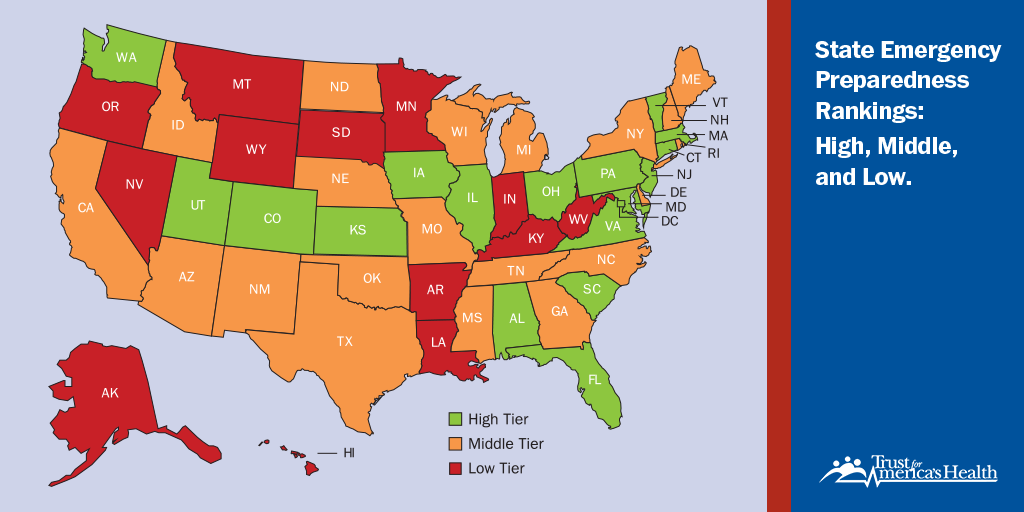
The report tiers states and the District of Columbia into three performance levels: high, middle and low, placing 17 states and DC in the high-performance tier, 20 states in the middle performance tier, and 13 states in the low performance tier based on their 2021 performance.
States' Performance by Tiers
| Performance Tier | States | Number of States |
| High Tier | AL, CO, CT, DC, FL, IL, IA, KS, MD, MA, NJ, OH, PA, SC, UT, VA, VT, WA | 17 states and DC |
| Middle Tier | AZ, CA, DE, GA, ID, ME, MI, MO, MS, NE, NH, NM, NY, NC, ND, OK, RI, TN, TX, WI | 20 states |
| Low Tier | AK, AR, HI, IN, KY, LA, MN, MT, NV, OR, SD, WV, WY | 13 states |
Overall, 12 states improved their performance while 16 states slipped in their ranking. All states’ performance is relative to that of other states.
Three states, Ohio, Pennsylvania and South Carolina, improved their performance by two tiers.
Nine states improved by one tier: Alabama, Arizona, Florida, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, New Hampshire, New Jersey, and New York.
Sixteen states fell one tier: Delaware, Georgia, Idaho, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Minnesota, Mississippi, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, and Wisconsin.
In addition, the report found:
- A majority of states had plans in place to expand healthcare and public health laboratory capabilities in an emergency.
- Most states are accredited in the areas of public health, emergency management or both.
- A large majority of Americans who receive their household water through a community water system had access to safe water.
- Only about half of the U.S. population is served by a comprehensive local public health system.
- Seasonal flu vaccination rates have risen significantly in recent years but are still lower than the goal set by Healthy People 2030.
- Just over half of workers used some kind of paid time-off in a one-month sample. The need for paid time off has become particularly apparent during the pandemic, as many workers became ill or needed to care for a sick family member.
- Only 28 percent of hospitals, on average, earned a top-quality patient safety grade during the year, down from 31 percent the year prior.
The report measured states’ performance during a year that presented intense demands on the nation’s public health system. In addition to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, 2021 saw record heat in many places, extensive flooding, wildfires throughout the Western U.S., a highly active hurricane season, and unusual and deadly December tornados in eight states. At the same time, hundreds of public health officials having experienced burn-out, threats to their safety, and attempts to limit their public health authorities have resigned, retired, or been fired.
While critical progress was made in fighting COVID-19 during 2021, particularly through the widespread availability of vaccines and a more coordinated federal response, the pandemic continued to illuminate the ways in which health inequities put communities of color and low-income communities at heightened risk for worse health outcomes during an emergency.
“Social, economic, and health inequities undermine a community’s ability to prepare for, respond to, and recover from a public health emergency. If we enter the next public health crisis with the same magnitude of health inequities in our communities as has been evident during this pandemic, the impact will be similar: preventable loss of life, disproportionate impact on communities of color and low-income communities, and widespread social and economic disruption. It is impossible to separate strong public health emergency preparedness and health equity,” said J. Nadine Gracia, M.D., MSCE, President and CEO of Trust for America’s Health.
Among the report's policy recommendations were:
- Congress and states should provide stable, flexible, and sufficient funding for public health, including for infrastructure, data systems, and the public health workforce.
- Congress should create a COVID-19 Commission to review and address gaps in the pandemic response, and leaders at all levels of government should reject attempts to weaken public health authorities.
- Policymakers should take steps to prevent disease outbreaks by investing in vaccination infrastructure, antibiotic resistance programs, and by providing paid leave for all workers.
- Congress should create programs to help build resilient communities by investing in health equity and the social determinants of health, including anti-poverty programs and programs that build financial security for families.
- Congress should invest in the development and distribution of medical countermeasures to enable rapid development and effective deployment of life-saving products during emergencies and federal and state policymakers and healthcare systems leaders should work together to prioritize effective coordination and communication during emergencies.
- The White House, Congress, and states should develop plans and provide funding to minimize the health impacts of climate change and do so in ways that address health equity.
Read the Full Report |

